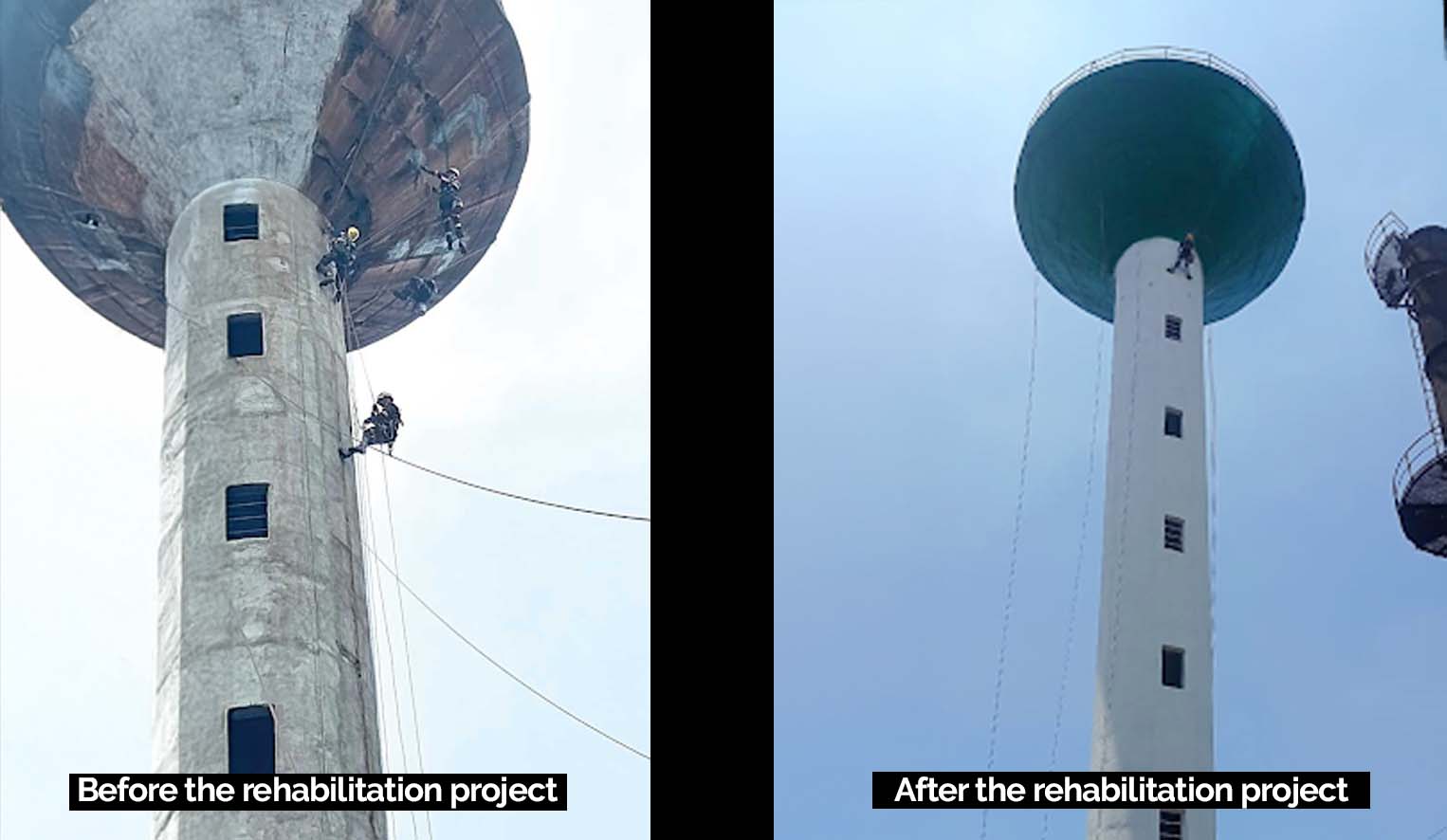
Introduction
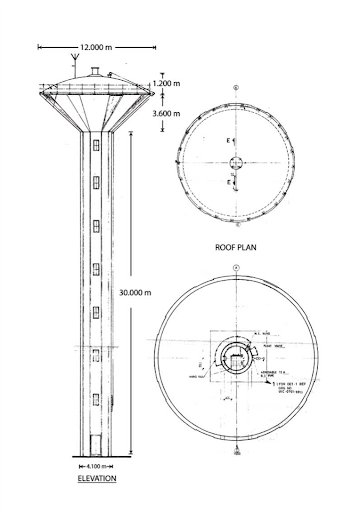
The RCC overhead water tank at TSLPL plays a critical role in supplying water for process operations. Over time, structural distress, such as cracks in the ring beams and columns, threatened the integrity of the tank. A comprehensive rehabilitation was undertaken, leveraging advanced techniques like rope access and work at height solutions to ensure safety, efficiency, and effectiveness during the repair process.
The Issue
A visual inspection revealed extensive cracking in the tank. The outer side walls exhibited more pronounced cracks compared to the inner walls. Additionally, signs of chlorination and concrete degradation were evident inside the upper water tank. These issues compromised the structural reliability and functionality of the tank.
Structural Assessment
To evaluate the extent of the damage, non-destructive testing (NDT) was conducted, with rope access technicians enabling inspections of challenging, elevated areas. The tests included:
● Rebound Hammer Test to assess concrete hardness and strength.
● Carbonation Test to measure carbonation depth and detect deterioration.
● Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test to locate cracks and evaluate concrete quality.
● Rebar Mapping to identify the condition of reinforcement bars.
● Chemical Tests to analyse concrete composition.
The results confirmed structural weaknesses, with significant cracks and deteriorated concrete in various sections.
Solution Provided
The repair process employed rope access and work at height techniques, ensuring safe and efficient access to the damaged areas. Key steps included:
1. Concrete Removal: Degraded concrete was carefully chipped away.
2. Surface Preparation: Exposed steel was cleaned and treated with a rust remover compound.
3. Corrosion Protection: Two coats of epoxy-based zinc primer were applied to reinforce corrosion resistance.
4. Bonding Agent Application: An epoxy bonding agent was used to secure adhesion with the new material.
5. Polymer Modified Mortar (PMM): The cracks and damaged areas were restored using PMM, ensuring structural integrity and durability.
Conclusion
The rehabilitation project restored the RCC water tank’s strength and functionality. Rope access and work at height methods proved instrumental, enabling precise, safe, and efficient repairs in elevated and confined spaces. By addressing structural concerns with advanced materials and techniques, the tank was returned to operational reliability, ensuring its longevity and performance for years to come.



