Green Energy
Harnessing Industrial Waste Heat
Waste heat energy represents a huge yet largely untapped resource in the industry. If energy lost from the large quantities of hot excess gases from furnaces, flare stacks, boilers, kilns, and ovens could be captured and recovered, then considerable amounts of primary fuel could be saved. A key challenge is often the intermittent and/or variable nature of the waste heat source, while the potential application of the captured energy needs to be continuous and non-variable.
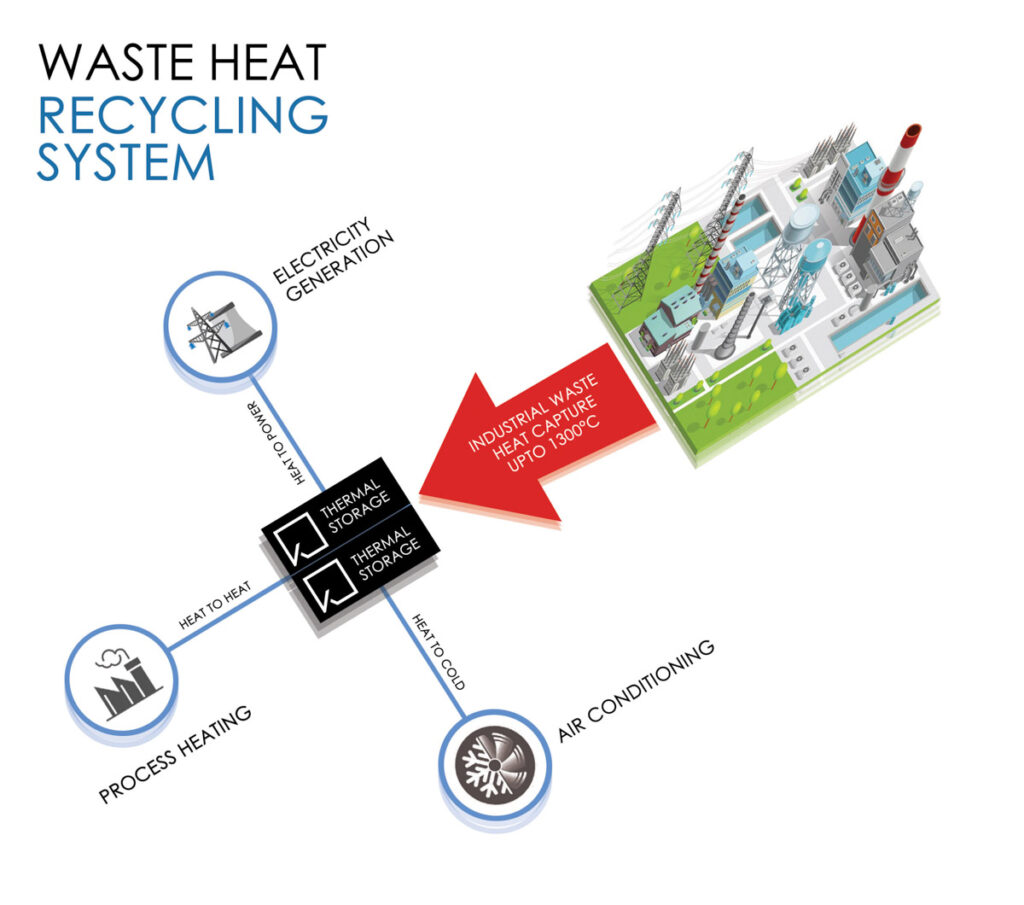
How does the technology work?
A Thermal Energy Storage (TES) system solves this “phasing” problem between source and application. Our partnership with KraftblockTM, Germany, brings a unique TES technology to market that allows the capture and storage of high-grade heat from industrial processes up to 1300 °C. Instead of letting waste heat go unharnessed into the atmosphere, the KraftblockTM TES recycles it with its Waste Heat Recycling Storage System. The reuse of waste heat represents a climate-neutral energy source and enables industries to use this captured energy for process heat, steam generation, electricity, or cooling.
Modular
Scalable energy storage from 4 MWh and above
Energy Density
1.2 MWh/m3 (3x higher than competition)
Sustainable Technology
Durable
Economical
Amortisation period less than 3 years
Innovative thermal storage system
At its core is a storage material that combines high thermal conductivity with high specific heat capacity and can store temperatures up to 1300 °C in a modularised and scalable format. We are engineering and implementing this Green Energy solution in the heavy industry enabling substantial primary fuel savings and significant CO2 emissions reduction for our customers.
The overall function of the TES is simple
Charging – heat is transferred from the heat transfer medium to the granulate (storage material), where it is stored.
Discharging – To access the energy as needed, the charging process is reversed: An ambient transfer medium is made to flow through the hot granulate and extracts the thermal energy.

Image Copyright © Kraftblock

